Where (as well as how and why) do I find the Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) on my new car and why is it so darned important when buying car insurance? You may be asking yourself this question as you try to hunt and peck this way-too-long code onto a car insurance online registration page.
The answers to these VIN questions can be quite complicated and yet it is also rather simple. The VIN, messy jumble of numbers and letters that it is, is your car’s DNA imprint in the world of car manufacturing, buying, selling and re-selling. Until your new vehicle’s very last day as a road-worthy vehicle, this “VIN number” marks it with a one-of-a-kind stamp.
How to Find Your VIN Number
Your vehicle’s 17-character identification code is also the manufacturer’s serial number. The VIN becomes important every time you get your car registered, buy car insurance, have an accident or sell your car.
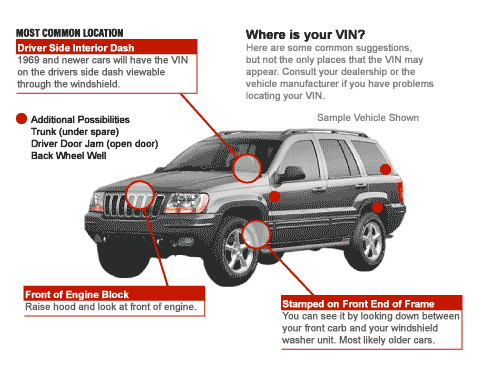
But where do you find the VIN? It’s not always located in same spot in every vehicle. So, here’s where you can check to find it:
- On the interior dash just below the windshield
- On the driver’s side of the front wheel arch
- On the steering column just below the steering wheel
- On the driver or front passenger inner door panel in what is known as the “firewall”
- Under the hood along a radiator support bracket or on the engine’s frame
- Inside the vehicle’s maintenance book
What Does It All Mean?
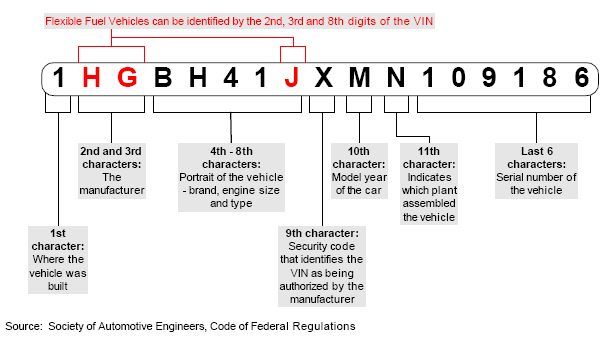
A vehicle’s identification number (VIN) tells the story of the car in 17 “characters” (either numbers or letters), including:
First Characters: The first three characters together are called the World Manufacturer’s Identification or WMI. The first character of the WMI denotes the country in which the vehicle was manufactured. For example, VINs that start with 1 are used for vehicles built in the United States of America; VINs beginning with J are used for vehicles manufactured in Japan.
Second and Third Characters: These two characters denote the manufacturer and make of the vehicle. Each manufacturer is assigned its own unique codes. For example, a VIN beginning with 1GC indicates that it was manufactured in the United States (1), by General Motors (G), and is part of GM’s Chevrolet line (C). A VIN that starts with JT2 signifies that the vehicle was manufactured in Japan (J), by Toyota (T), and is part of Toyota’s passenger car line (2).
Fourth through Eighth Characters: The next five characters are called the Vehicle Description Section (VDS) and identify specific equipment such as engine type, restraint system, body style and braking system.
Ninth Character: The Check Digit is a mathematical algorithm developed by the Department of Transportation (DOT) to check the accuracy of the previous VIN numbers.
Tenth Character: This identifies the year of the vehicle. For example, a 7 may indicated the car was built in 2007. Vehicles built before 1991 are identified by a letter starting with A for 1980.
Eleventh Character: This character identifies the manufacturing plant in which the vehicle was assembled.
Last Six Characters: The last six characters of the VIN are the vehicle’s actual serial number. This is a unique identifier by each manufacturer.
Still confused? Don’t be. Your VIN number also shows up on your DMV registration and your insurance card. Just keep both documents in your glove compartment and a copy of each in your files at home.